|
|
Introduction
The coexistence of equipment of different technologies and the inadequacy of the installations favors the emission of electro-magnetic energy and often causes problems of electro-magnetic compatibility.
EMI is the energy that causes undesirable response to any equipment and may be generated by sparking on the motor brushes, tension circuits switching, activation of inductive and resistive loads, activation of switches, circuit breakers, fluorescent bulbs, heaters, automotive ignitions, atmospheric discharges and even the electrostatic discharge between persons and equipment, microwaves devices, mobile communication equipment etc. All this may provoke alterations with the resulting overload, sub-voltage, peaks, voltage transients etc., which may cause high impact on a communication network. This is very common in industries and factories, where EMI is fairly frequent in function of the larger use of machines such as welding instruments, motors (MCCs) and in digital networks and computers in the vicinity of these areas.
The biggest problem caused by EMI is the occasional situations that slowly degrade the equipment and its components. Many different problems may be generated by EMI on electronic equipment as communication failures between devices of the same equipment network and/or computers, alarms produced without explanation, action on relays that do not follow logic, without being commanded, in addition to the burning of electronic components and circuits etc. It is very common the occurrence of noises in power source lines due to bad grounding and shielding or even error in the project.
The topology and the distribution of the wiring, types of cables, protection techniques are factors that must be considered to minimize the EMI effects. Keep in mind that in high frequencies the cables work as a transmission system with crossed and confused lines, reflect and scatter energy from one circuit to another. Keep the connections in good conditions. Inactive connectors may develop resistance or become RF detectors.
A typical example of how the EMI may affect the work of an electronic component is a capacitor exposed to a voltage peak higher than its specified nominal voltage. This may deteriorate the dielectric, whose width is limited by the capacitor operation voltage, which may produce a gradient of potential inferior to the dielectric rigidity of the material, causing malfunctioning and even the capacitor burning. Or, still, the transistor polarization currents may be altered and cause their saturation or cut, or burn its components by the joule effect, depending on the intensity.
In measurements:
- Do not be neglectful, imprudent, irresponsibly inexpert or incompetent on technical problems.
- Remember that each plant and system has its own safety details. Get well informed about them before starting work.
- Whenever possible refer to the physical regulations, as well as the safety practices for each area.
- Act safely on measurements, avoiding contact between terminals and wiring, as high voltage may cause electric shock.
- In order to minimize the risk of potential problems related to safety, comply with the safety standards and those of the local classified areas regulating the equipment installation and operation. These standards vary according to the area and are being constantly updated. The user is responsible to determine which rules to follow in his applications and guarantee that each device is installed in compliance with them.
- The inadequate installation or use of equipment in non-recommended applications may damage the system performance and consequently the process, as well as be a source of danger and accidents. Therefore, only use trained and qualified professionals on installation, operation and maintenance jobs.
Quite often the reliability of a control system is jeopardized by its poor installations. Commonly, users tolerate them but a close look reveals problems involving cables, their courses and packing, shielding and grounding.
It is extremely important that every person involved is aware and conscious and moreover committed with the plant operational reliability and personal safety. This article provides information and tips on grounding but in case of doubt the local regulations always prevail.
The control of noises in automation systems is vital, as it may become a serious problem even with the best devices and hardware to collect data and work.
Any industrial environment has electric noises in sources, including AC power lines, radio signals, machines and stations etc.
Fortunately, simple devices and techniques as the use of adequate grounding methods, shielding, twisted wires, the average signal method, filters and differential amplifiers may control noise on most measurements.
Frequency inverters have commuting systems that may generate electromagnetic interference (EMI). Their amplifiers may emit a significant EMI on 10 MHz to 300 MHz frequencies. Most probably this commuting noise may produce intermittence in nearby equipment. While most manufacturers take due precaution on their projects to minimize this effect, the complete immunity is not attainable. So, some layout, wiring, grounding and shielding techniques offer a significant contribution to this optimization.
The EMI reduction will minimize initial and future operation costs and problems on any system.
This article shows how noises can be minimized by shielding. Let’s deal about capacitive coupling.
Capacitive Coupling
If the noise is caused by an electric field, the shield is efficient, as there will be no Q2 inside the closed and grounded enclosure.
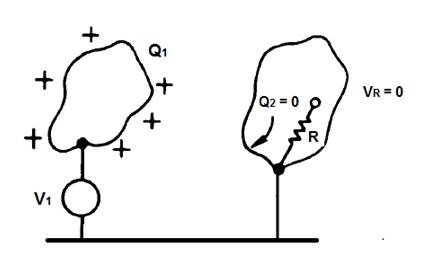
Figure 1 – The Q1 Load does not create loads in a closed and grounded metal enclosure.
An electric field coupling is modeled as a capacitance between two circuits (see figure 2). Figure 3 shows the physical model.
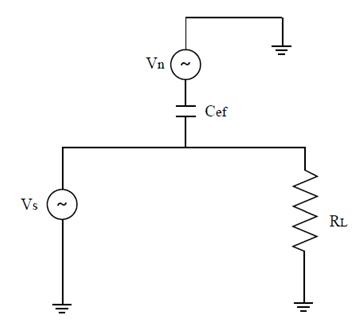
Figure 2 – Circuit equivalent to the capacitive coupling
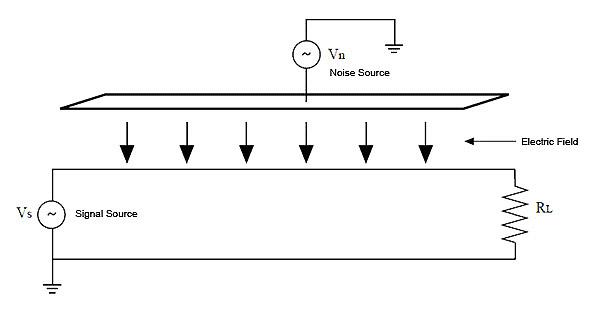
Figure 3 – Capacitive coupling physical representation
The equivalent capacitance, Cef, is directly proportional to the electric field area of action and inversely proportional to the distance between the two circuits. Therefore, by widening the separation or narrowing the area, the CEF influence will be minimized and the capacitive coupling will not affect the signal too much. This is the effect of the capacitance between two bodies with electric loads separated by one dielectric, which is called mutual capacitance effect.
The capacitive coupling level is proportional to the noise signal frequency and amplitude.
The electric field effect is proportional to the frequency and inversely proportional to the distance.
The disturbance level depends on the voltage variations (dv/dt) and the value of the coupling capacitance between the “disturbing cable” and the “victim cable.”
The coupling capacitance increases with:
- The frequency inverse: The capacitive coupling potential increases as the frequency increases (the capacitive reactance, considered as capacitance coupling resistance decreases according to the frequency and may be seen in the XC = 1/2πfC) formula.
- The distance between the disturbing and victim cables and the length of the cables that run in parallel.
- The cable height in relation to plan of reference (in relation to the ground).
- The input impedance of the victim circuit (circuits of high input impedance are most vulnerable).
- The insulation of the victim cable (εr of the cable insulation), mainly in strongly coupled pair of cables.
The influence may be reduced by the adequate use of the shield, which will work as a shielding (Faraday cage). The shielding must be placed between the capacitive coupled conductors and connected to ground only at one point, beside the signal source. See figure 5. Figure 4 shows an inadequate condition whose loop current circulates by the shield.
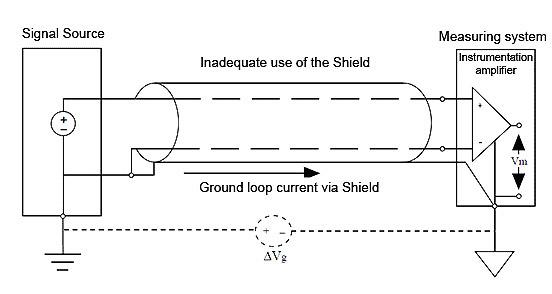
Figure 4 – Inadequate use of the shield, grounded at more than one point.
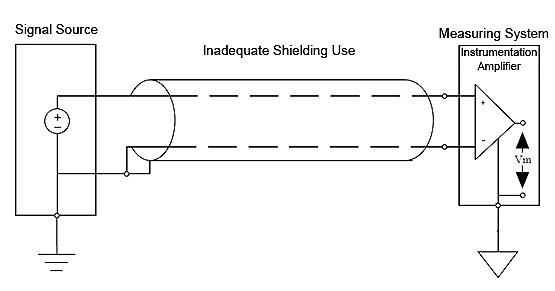
Figure 5 – Inadequate use of shielding, grounded at only one point.
Measures to reduce the capacitive coupling effect
- Limit the length of the cable running in parallel
- Increase the distance between the disturbing cable and the victim cable.
- Ground one of the extremities of the Shields on both cables
- Reduce the dv/dt of the disturbing signal, by increasing the signal raising time, whenever possible (lower the signal frequency)
- Whenever possible protect the conductor or equipment with metal material (Faraday shielding). The ideal is to cover one hundred per cent of the part to be protected and to ground this shielding so that the parasite capacitance between the conductor and the shield does not work as another power supply or crosstalk element. Figure 6 shows the interference between cables, whose capacitive coupling between cables induces voltage transients (electrostatic pickups). In this situation the interference current is drained to ground through the shield, without affecting the signal levels.
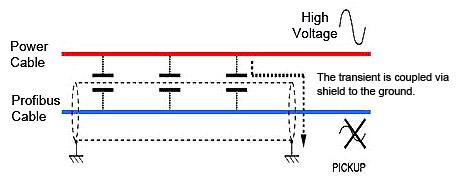
Figure 6 – Interference between cables: the capacitive coupling induces voltage transients (electrostatic pickups)
Figure 7 shows an example of protection against transients.
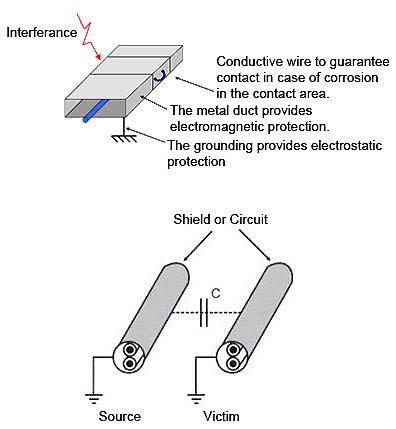
Figure 7 – Example of protection against transients (Best solution against Foucault Current)
How to reduce electrostatic interference:
- Adequate grounding and shielding
- Optical insulation
- By using grounded metal ducts and boxes
Figure 8 shows the coupling capacitance between two conductors separated by a D distance.
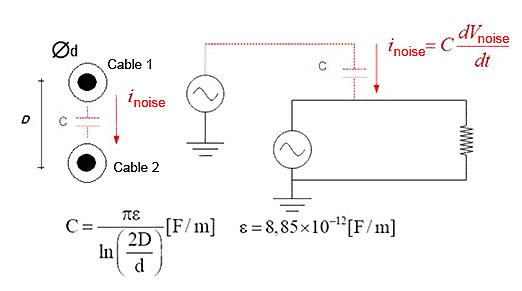
Figure 8 - Capacitive coupling between conductors at a D distance
Shielding
Grounding and shielding are mandatory to guarantee the integrity of a plant data. In practice, it is very common finding intermittent work and gross errors in measurements due to bad installations.
Noise effects can be reduced with adequate project, installation, cable distribution, grounding and shielding techniques. Inadequate grounding can be the source of undesired and dangerous potentials that may impair the effective operation of the equipment or the system itself.
The shield must be connected to the signal of the reference potential it is protecting (see figure 9).
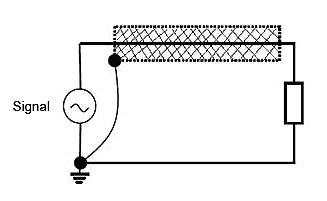
Figure 9 – Shielding connected to the reference potential of the signal it is protecting
When having multiple segments, keep them connected to guarantee the same reference potential, as shown on figure 10.
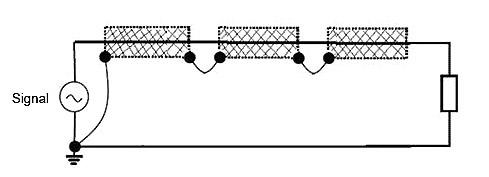
Figure 10 – Multiple-segment shielding connected to the reference potential of the signal it is protecting
Shielding vs Grounding at a Single Point
In this case the current will not circulate by the loop and will not cancel the electric fields.
The length of the conductor extending out of the shield must be reduced to guarantee good shield connection to the ground.
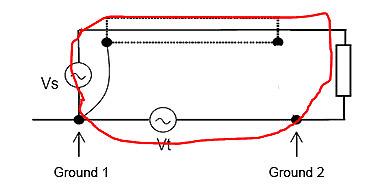
Figure 11 - Shielding vs grounding effect at a single-point
Shielding vs. Grounding Effect at Two Points
The currents are distributed in function of their frequencies, because they follow the path with least impedance.
Up to a few kHz: the inductive reactance is negligible and the current will flow by the path with least resistance.
Above kHz: the inductive reactance predominates and the current will circulate by the path with least inductance.
The path with least impedance is the one whose return course is near the departing course, as it presents the largest distributed capacitance and the least distributed inductance.
The length of the conductor extending out of the shield must be reduced to guarantee good shield connection to the ground.
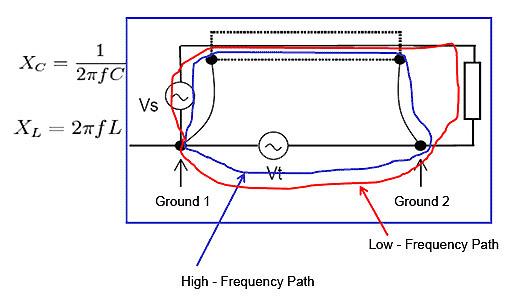
Figure 12 – Shielding vs. grounding effect at two points
It is worth mentioning:
- There is no protection against ground loops.
- Possibility of significant damages to the active equipment when the ground potential difference between both ends exceeds 1 V (rms).
- The grounding electrical resistance must be the lowest possible on both ends of the segment to minimize the ground loops, mainly in low frequencies.
Cable shielding is used to eliminate capacitive coupling interferences caused by electric fields.
The shielding only is efficient when it establishes a low impedance path to the ground.
A floating shield does not protect against interferences.
The shield loop must be connected to the reference potential (ground) of the circuit that is being shielded.
Ground the shielding at more than one point may be problematic.
Minimize the length of the shielding-reference connection, as it works as a coil.
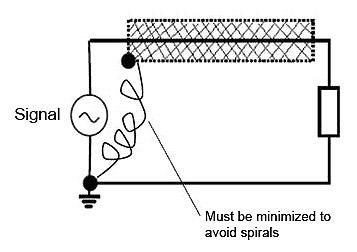
Figura 13 – The shielding-reference length must be reduced as it works as a coil.
Electrical fields are much easier to shield than magnetic fields, and the use of shielding at one or more points works against electrical fields.
The use of non-magnetic metals around the conductors does not shield against magnetic fields.
The key to magnetic shielding is to reduce the loop area. Use a twisted pair or the return of the current through the shielding.
To prevent the radiation on a conductor, a grounded shielding on both sides is normally used above the cut frequency, although a few precautions should be taken.
Only a limited quantity of magnetic noise can be shielded because of the ground loop that is formed.
Any shielding that conducts a noise current must not be part of the signal path.
Use a shielded twisted cable or a tri-axial cable on low frequencies.
The effectiveness of the twisted cable shielding increases with the number of turns.
Conclusion
next articles we will see details on inductive coupling. Every automation project must take into consideration the standards that guarantee adequate signal levels, in addition to the safety required by the application. Recommended is to annually carry out preventive maintenance actions and check each grounding system connection that must guarantee the quality of each connection in relation to robustness, reliability and low impedance. Make sure there is no contamination and corrosion.
This article does not replace NBR 5410, NBR 5418, and IEC 61158 and IEC 61784 standards nor PROFIBUS profiles and technical guides. In case of discrepancies or doubts, the IEC 61158 and IEC 61784 standards, and the profiles, technical guides and manufacturer manuals prevail. Whenever possible, refer to EN50170 for physical regulations as well as for safety practices on each area.
Bibliographic References
- Technical articles - César Cassiolato
- https://www.smar.com.br/en/system302
- https://www.smar.com.br/en
- www.smar.com.br/en/technical-articles
- http://www.electrical-installation.org/wiki/Coupling_mechanisms_and_counter-measures
- National Application Notes 25: Field Wiring and Noise Considerations for Analog Signals - Syed Jaffar Shah
- Grounding, Shielding, Noises and Installation Tips - César Cassiolato
- The use of Metal Ducts Minimizing the Foucaualt Currents in PROFIBUS installations - César Cassiolato
- Noises and Interferences in PROFIBUS Installations - César Cassiolato
- https://www.smar.com.br/en/technical-article/tips-on-shielding-and-grounding-in-industrial-automation
- Pesquisas na internet (Todas as ilustrações, marcas e produtos usados aqui pertencem aos seus respectivos proprietários, assim como qualquer outra forma de propriedade intelectual).
Related Links
Access the complete list of SMAR technical articles.
- César Cassiolato was Director of Marketing, Quality and Engineering Projects & Services of Nova Smar S/A, was the President of the PROFIBUS Brazil-Latinamerica Association (2006 – 2010), Technical Director of the PROFIBUS Competence and Training Center, Director of the FDT Group in Brazil, and is a Certified Engineer on PROFIBUS Technology and PROFIBUS Installations from Manchester University.


